Damage is typically the result of deamination, alkylation, hydroxylation, or attack by an oxygen free radical, while the incorrect base can be uracil substituted for thymine. • C to T • C to U • T U mismatch •
In secondary antibody diversification within the adaptive immune response, activation-induced (cytidine) deaminase (AID) is involved in the initiation of three distinct immunoglobulin diversification processes: somatic hypermutation (SHM), class-switch recombination (CSR), and gene-conversion (GC). AID-catalyzed deamination of deoxycytidine creates a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the DNA strand by generating a uracil:guanine mismatch. A high-fidelity base excision repair enzyme, uracil-DNA glycosylase (UNG2), excises the alien uracil nucleobase, then error-prone DNA polymerases complete the base-excision repair. During this base-excision repair, incorrect nucleobases may be substituted at or adjacent to the original C to U mutation site. Mispairing (transition) mutations are susceptible to indels - insertions and deletions. (Such mutation vulnerable areas in the genome are termed 'hotspots', and they have played a significant role in biological evolution.)
Oxidative DNA lesions induced by oxygen free radicals such as superoxide and hydroxyl radicals appear to be repaired predominantly by base excision repair mechanisms. Further, BER is the major DNA repair system involved in removal of various oxidative DNA lesions induced by ionizing radiation - these include abasic sites and modified DNA base and sugar residues.
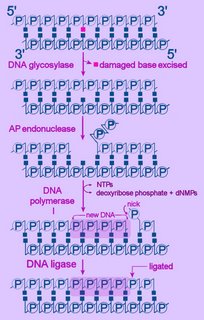 Left - diagram of base excision repair - click to enlarge image.
Left - diagram of base excision repair - click to enlarge image.NTPs = ribonucleoside triphosphates
dNMP = deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate
First, the altered base is excised by a specific DNA glycosylase, which breaks the beta N-glycosidic bond and creates an AP, or abasic site. This site is identical to that generated by spontaneous depyrimidination or depurination. Six DNA glycosylases have been identified in humans – each excises an overlapping subset of either spontaneously formed (such as hypoxanthine), oxidized (such as 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine), alkylated (such as 3-methyladenine), or mismatched (for example, T:G) bases.
Next, the terminal sugar-phosphate is removed by an AP endonuclease (Ape1), leaving a 3’-OH terminal and an abnormal 5'-abasic terminus. The resulting gap is refilled by the 5’-deoxyribose-phosphodiesterase action of a DNA polymerase I (DNA polymerase beta in mammals), then the strands are re-ligated by DNA Ligase I or a complex of XRCC1 and LigIII.
An alternative BER pathway corrects errors involving more than one nucleotide. The Fen1 protein excises the long-patch structure that is produced by DNA polymerase strand displacement. This "long-patch" repair process is divided into two subpathways: a PCNA-stimulated, Pol-beta-directed pathway and a PCNA-dependent, Pol-delta/epsilon -directed pathway.
Also: DNA repair : exogenous nucleobase rescue of abasic substitutions : link to table - human DNA repair genes : diagram>BER
▲ Top ▲
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.